Describe the General Structure of an Amino Acid
Amino acids are molecules used to build proteins. Genes are the specific codes of these amino acids which produces a protein and alleles is the.

Structure Of Glycine Which Is A Simple Amino Acid Download Scientific Diagram
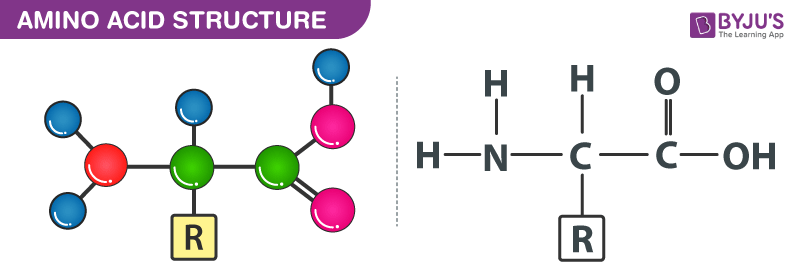
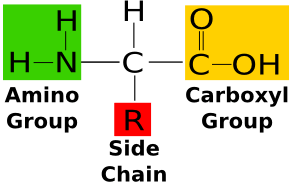
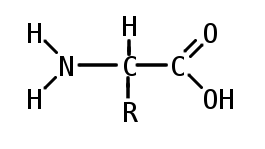
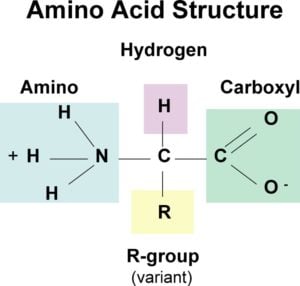
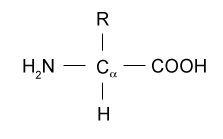
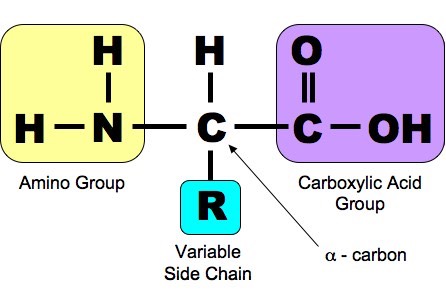
A carbon the alpha carbon A hydrogen atom H A Carboxyl group -COOH An Amino group -NH 2 A variable group or R group.
. All amino acids contain a carbon atom in the middle of the molecule the alpha-carbon. An amino acid consists of a central or alpha carbon atom attached to an amino group NH2 a carboxylic acid group COOH a hydrogen atom and a variable side group called the R group. The general formula for an amino acid is given below.
1 What Does The Term Amino Acid Signify About The Structure Of The Molecule. A central carbon atom is bound to an amino group carboxyl group a. The third group is denoted by R.
A water molecule is removed by releasing an OH from carboxyl group of one amino acid and hydrogen from the amino group of another amino acid. Generally amino acids have the following structural properties. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins.
All amino acids include 5 basic parts. The basic structure of an amino acid an amino acid consists of one central carbon. Amino acids are a type of organic acid that contains both a carboxyl group COOH and an amino group NH 2.
Structure of an Amino Acid. An amino group a carboxyl group a hydrogen atom and a variable group symbolised by R. Amino acids are the monomers that comprise polypeptides polypeptides being the polymers.
All amino acids have a central carbon atom. The simplest and smallest amino acid found in proteins is glycine for which the R-group is a hydrogen H. This R group makes the amino acid unique.
L-amino acids are the form of stereoisomers used by the cells to produce proteinsThey occur in all proteins produced by. All amino acids found in protein have a basic structure which differ only in the structure of the R-group or the side chain. The R group also known as a side chain is different for each.
Solution for Describe in detail the processes of transpiration and water uptake in a plant. Any carbon atom other than that of the carboxyl COOH. All amino acids found in proteins have this basic structure differing only in the structure of the R-group or the side chain.
6 How does the structure of amino acids relate to its function. An amino acid is an organic molecule that is made up of a basic amino group NH 2 an acidic carboxyl group COOH and an organic R group or side chain that is unique to each amino acid. Amino acids join together in an enzyme-catalysed condensation reaction between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of.
Its which are bonded. 3 Why are molecules called amino acids. Are amino acids L or R.
One is an amine group -NH 2. For example as we have seen all of the common amino acids are L because they all have exactly the same structure including the position of the R group if we just write the R group as R. In the centre of the amino acid is an assymetric carbon atom called the alpha carbon.
A polypeptide folds into a 3D structure called a protein. The term amino acid is short for α-amino alpha-amino carboxylic acid. Basic Structure of an Amino Acid.
2 What is special about amino acid structure. The α carbon carboxylic acid and amino groups are common to all amino acids so the R. Describe the general structure of amino acids and the properties associated with the different side chains.
1 Describe the general structure of an L-a amino acid at pH 70 and draw its structure. Each molecule contains a central carbon C atom called the α-carbon to which both an amino and a carboxyl group are. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure which consists of a central carbon atom also known as the alpha α carbon bonded to an amino group NH 2 a carboxyl group COOH and to a hydrogen atom.
The second one is a carboxyl group -OOOH. 4 What is the basic molecular structure of amino acids quizlet. The carbon atom of the carboxyl group has a free bond to bond to nitrogen of the other amino group that now also has a free bond.
In the aqueous environment of the cell the both the amino group and the. Amino acids link together to form proteins. 5 How can amino acids be distinguished from one another.
Wat are te L amino acids. The R can represent one of 20 different side chains. 2 Using the 5 categories into which the 20 naturally occurring amino acids are classified draw the structure of one amino acid from each of the 5 categories of amino acids.
Although the neutrally-charged structure is commonly written it is inaccurate because the acidic COOH and basic NH 2 groups react with one another to form an internal salt called a zwitterion. The simplest and smallest amino acid is found in proteins is glycerin for which the R-group is a H hydrogen. This atom is surrounded by three chemical groups.
At the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the and attached to it are four groups a hydrogen a carboxylic acid group an amine group and an R-group sometimes referred to as a variable group or side chain. This carbon is covalently bonded to four different groups. Structure of Amino Acids.
This is the variable radical group and is different for every amino acid. A central carbon atom a hydrogen atom an amino group consisting of a nitrogen atom and two hydrogen atoms a carboxyl group consisting of a carbon atom two oxygen atoms and one hydrogen atom an R. Scientists use the name amino acid because these acids contain both amino group and carboxyl-acid-group in their basic structure.
All amino acids have the same basic structure shown in Figure 21. Antibody Basic Structure Function IgM IgD. What is the pka range for the carboxylic acid group and the amine group in amino acid.
Organic substances containing both amino and carboxylic groups are known as amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids and they all share the same general structure. Amino acids are the basic components of proteins.
Which of the following best describes the chemical structure of a typical amino acid found in a protein. Ah hydrogen carb oxalic acid group in the Mean group and another group thats different from all these usually different to say sometimes called the our group or sometimes called the side chain.

Amino Acid Formula Chemical Formula Of Amino Acid On Byju S
Amino Acids Properties Functions Sources And Its Deficiency Disorders
Amino Acids Mnemonics Epomedicine
Amino Acid New World Encyclopedia

Amino Acids Introduction To Chemistry
How Many Amino Acids Are There List Essential Benefits
2 2 Structure Function Amino Acids Biology Libretexts

General Structure Of A Amino Acid Download Scientific Diagram

Dr Ragaa Salama1 1 Amino Acids Objectives Define Amino Acids Describe The Chemical Nature Of Amino Acids List The Essential Semi Essential Non Essential Ppt Download

General Structural Formula Of Amino Acids Where R Can Be H Ch 3 Download Scientific Diagram
2 2 Structure Function Amino Acids Biology Libretexts

Amino Acid Standard Amino Acids Britannica

Amino Acids Structure Classification Properties With Videos Examples
Amino Acids Definition Properties Structure Classification Functions

General Structural Formula Of Amino Acids Where R Can Be H Ch 3 Download Scientific Diagram

Comments
Post a Comment